APOLLO LOGIN: https://pthscan.med.buffalo.edu/epmmwebportalnew/portal.php
Mystery Slide Case 1: John Smith
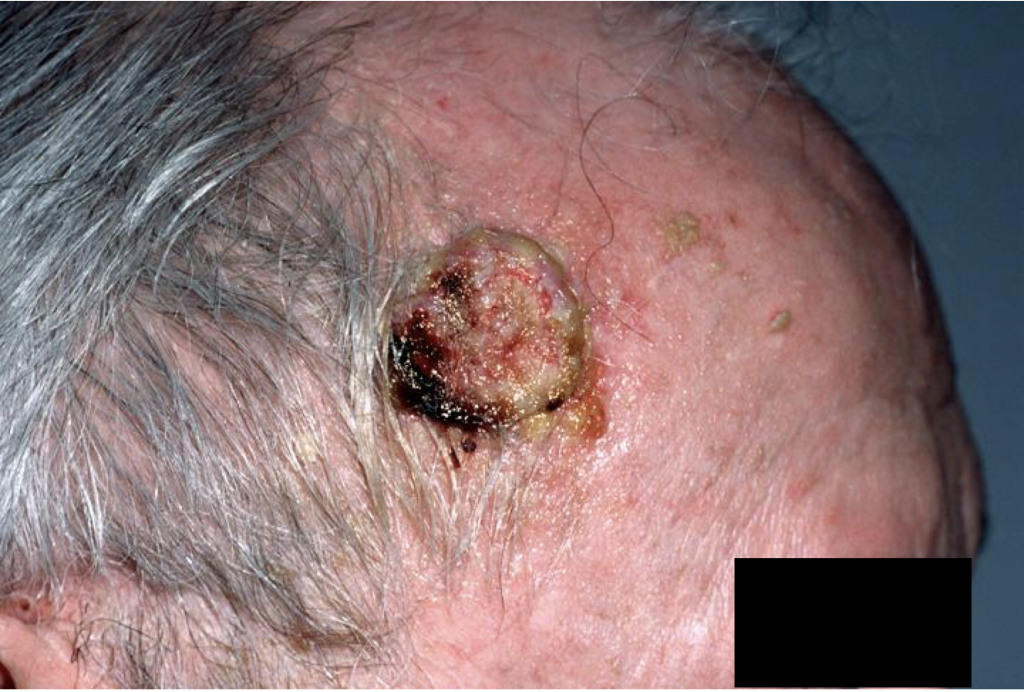 Clinical image: courtesy of Glenn Goldman, MD., Medscape, 2018
Clinical image: courtesy of Glenn Goldman, MD., Medscape, 2018
John Smith is a 72y/o man with ulcerated fungating growth on right temple, slowly growing over the past 2 years. Mr. Smith owns Schloss Alpli wines and is proud of the award winning Riesling wine he produces. He manages 25 acres of vines, doing the majority of the work himself including planting, harvesting, fermentation, and bottling. His wife is concerned about the “mushroom” on his head. Based on your integument knowledge, what typical and atypical histological features can be identified in Mr. Smith’s tissue biopsy? What cell types are involved? SEE MYSTERY SLIDE #1 (A1) on APOLLO
Identified as: Squamous Cell Carcinoma (SCC)
Structures identified (Refer to Mystery Slide A1 in Apollo):
- Hyperkeratinization at the surface of the gross specimen, which corresponds to the densely Eosinophilic staining of Keratin seen in the histological sample
- Well-progressed squamous cell carcinoma – we can determine it is epidermal tissue and can identify characteristic features of the epidermal strata (stratum spinosum etc.) in many areas of the tissue
Mystery Slide Case 2: Jane Doyle
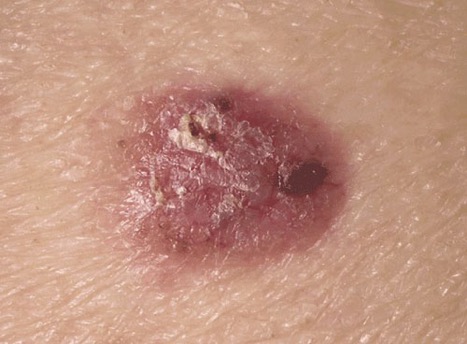
Image courtesy of Thomas Habif, MD
The above image is an erythematous 2.0 cm nodular lesion on the calf of a 52y/o woman, Jane Doyle. Ms. Doyle has an unremarkable medical history, takes no medication, and is a full partner in the law firm of Elegant Barristers, LLC. Her work is primarily as a medical malpractice attorney, defending physicians. As a teenager and through college she was employed as a lifeguard at the local country club pool in Tisbury, Massachussetts. While she loved being a lifeguard, she was concerned about sun exposure and the sunburns she experienced. This lesion has been growing over the past several years and bleeds on occasion. Based on your integument knowledge, what typical and atypical histological features can be identified in Ms. Doyle’s tissue biopsy? What cell types are involved? SEE MYSTERY SLIDE #2 (A2-4) on APOLLO
Identified as: Basal Cell Carcinoma (BCC)
Structures identified (Refer to Mystery Slide A2-4 in Apollo):
- A predominance of basophilic cells can be seen. They share a similarity in staining appearance to the stratum basale found in the right aspect of the specimen which contains healthy skin
- Below the basophilic clusters of cells, an infiltration of inflammatory cells can be seen which likely produces a redness of the skin seen in the gross specimen
Mystery Slide Case 3: J. Smith
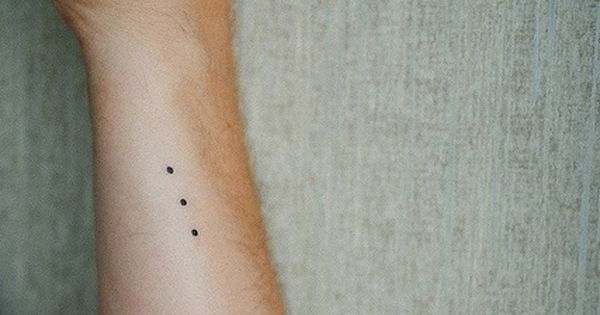
Several small dark nodules can be seen on the ventral surface of a patient’s forearm. The patient had been sailing throughout the Caribbean on a semester-at-sea experience and partying at every port along the way. After all the fun and sun, the patient noticed he had developed three unusual skin nodules. Upon docking in Fort Lauderdale, the patient decided to see a the doctor regarding the marks. A nodule was removed and sent to pathology for histological analysis. Based on your integument knowledge, what typical and atypical histological features can be identified in the patient’s tissue biopsy? What cell types are involved? SEE MYSTERY SLIDE #3 (Moore-Mystery Slide) on APOLLO
Identified as: Normal Skin Sample with Tattoo in Dermis
Structures identified (Refer to Moore-Mystery Slide in Apollo):
- The histological sample contains tattoo ink (India ink) pigment that has been phagocytosed by histiocytes (macrophages) found in the dermis of the skin.
- Notice the colour of the melanin in the keratinocytes of the epidermis is light brown where the dye in the dermis is very dark, and looks rather different from the melanin seen in the epidermis
- This slide demonstrates why tattoos are permanent due to the injection of tattoo ink below the dividing layer of cells (epidermis) into the dermis