Results
#1. The gland associated with the duct shown in the image uses which mode of secretion in order to release its secretory product?
Eccrine sweat glands secretions drain directly into the duct with no loss of cytoplasm or cell (Merocrine Secretion). Apocrine sweat glands also function through Merocrine secretion but empty into the hair follicle. The Sebaceous glands lose entire cells as a part of the secretory process (Holocrine Secretion).
#2. The stratum spinosum is also known as the “Prickle Cell” layer due to an abundance of which of the following features?
The stratum spinosum is characterized by keratinocytes with cytoplasmic extensions radiating from the cells. The keratinocytes are anchored to one another through desmosomes, which provide support to the epidermis.
#3. Which of the following images contains a Meissner’s corpuscle?
Section A: Ovarian Follicle
Section B: Meissner’s Corpuscle
Section C: Pacinian Corpuscle
Section D: Pacinian Corpuscle
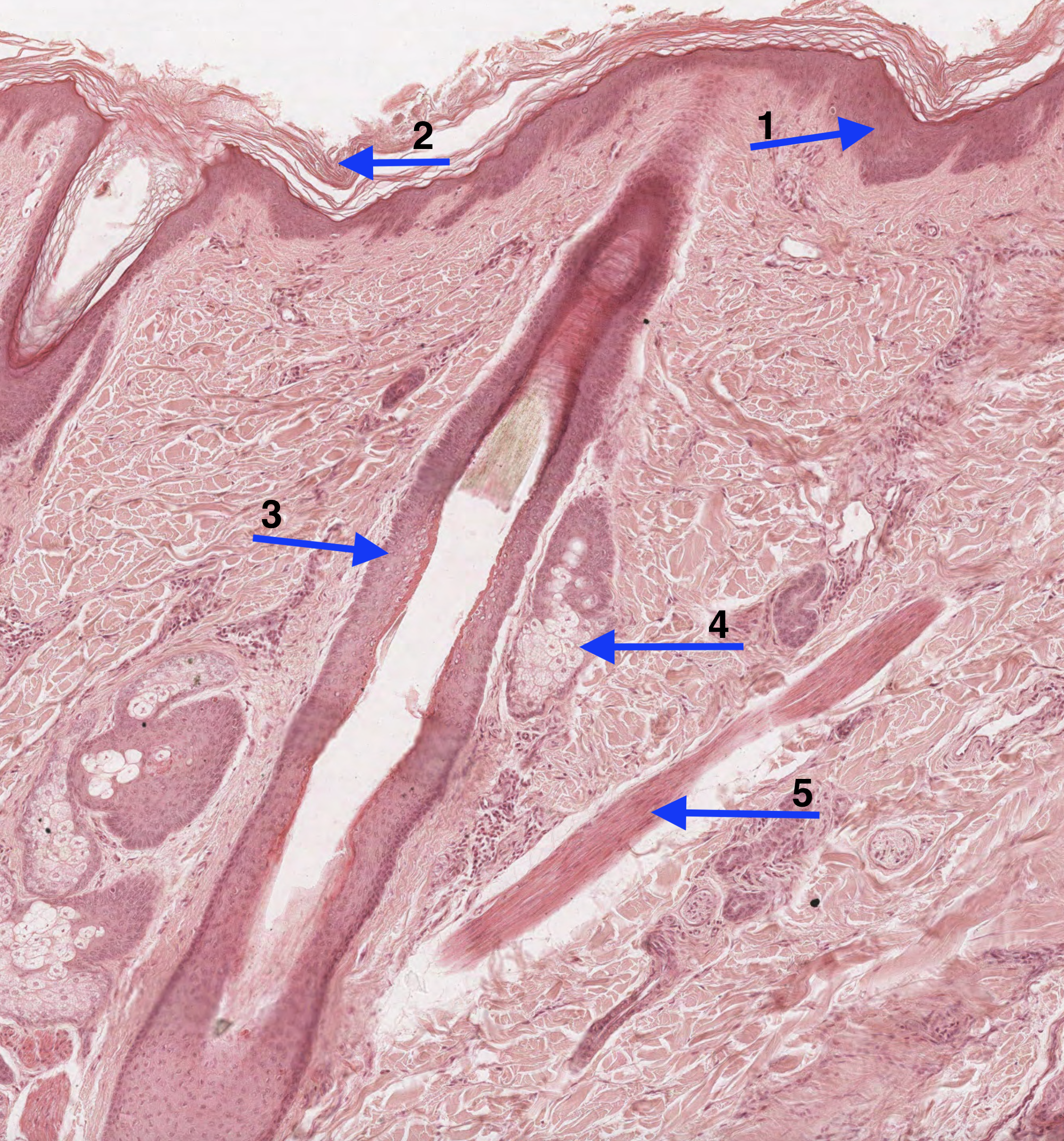
#4. The structure that is labelled as number 5 can be correctly described as a:
The arrow labelled number 5 indicates the arrector pili muscle which is attached to the hair follicle. This muscle is responsible for creating “goosebumps” on the skin. As the arrector pili muscle contracts, it forces the hair follicle into a more vertical position. The arrector pili is a smooth muscle, and thus under autonomic control by the sympathetic nervous system, which explain why the hairs “stand on end” during fearful situations.

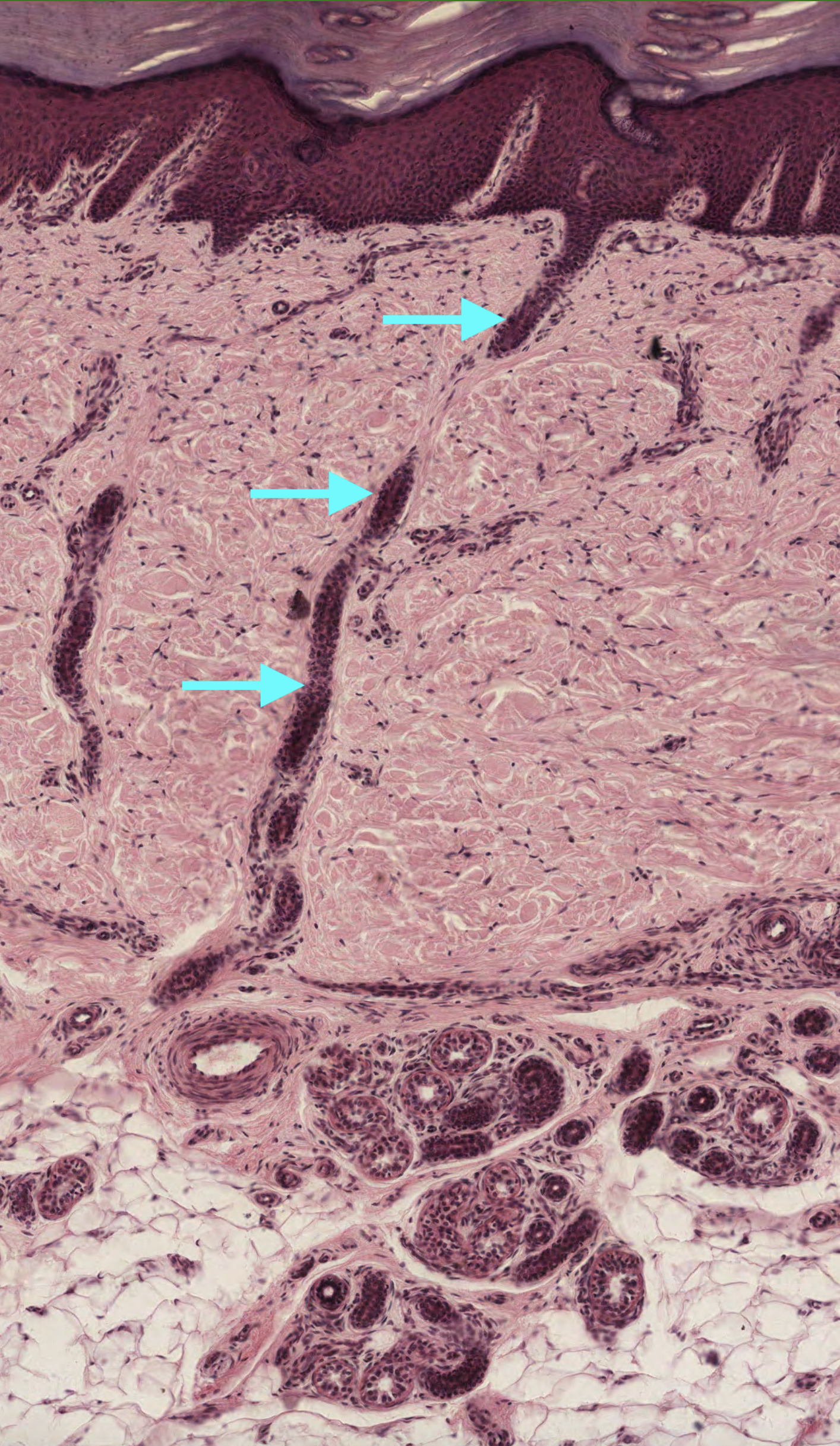
#5. The arrows indicate a _________________________________ passing through the dermis of the skin.
The arrows indicates a duct of an eccrine gland that reaches the surface of the skin. This duct is from an eccrine gland because it does not empty into a hair follicle, which is typically a feature seen in apocrine and sebeaceous sweat glands.
#6. There are three major types of glands found within the dermis of the skin. Which of the following do not drain their secretory product into the hair follicle?
Sebaceous glands and apocrine sweat glands both empty into hair follicles. The ducts of the apocrine sweat glands empty more superficially into hair follicle compared to the duct of sebaceous glands which drain slightly deeper along the hair follicle.
Eccrine sweat glands ducts open directly at the skin surface and not through a hair follicle.
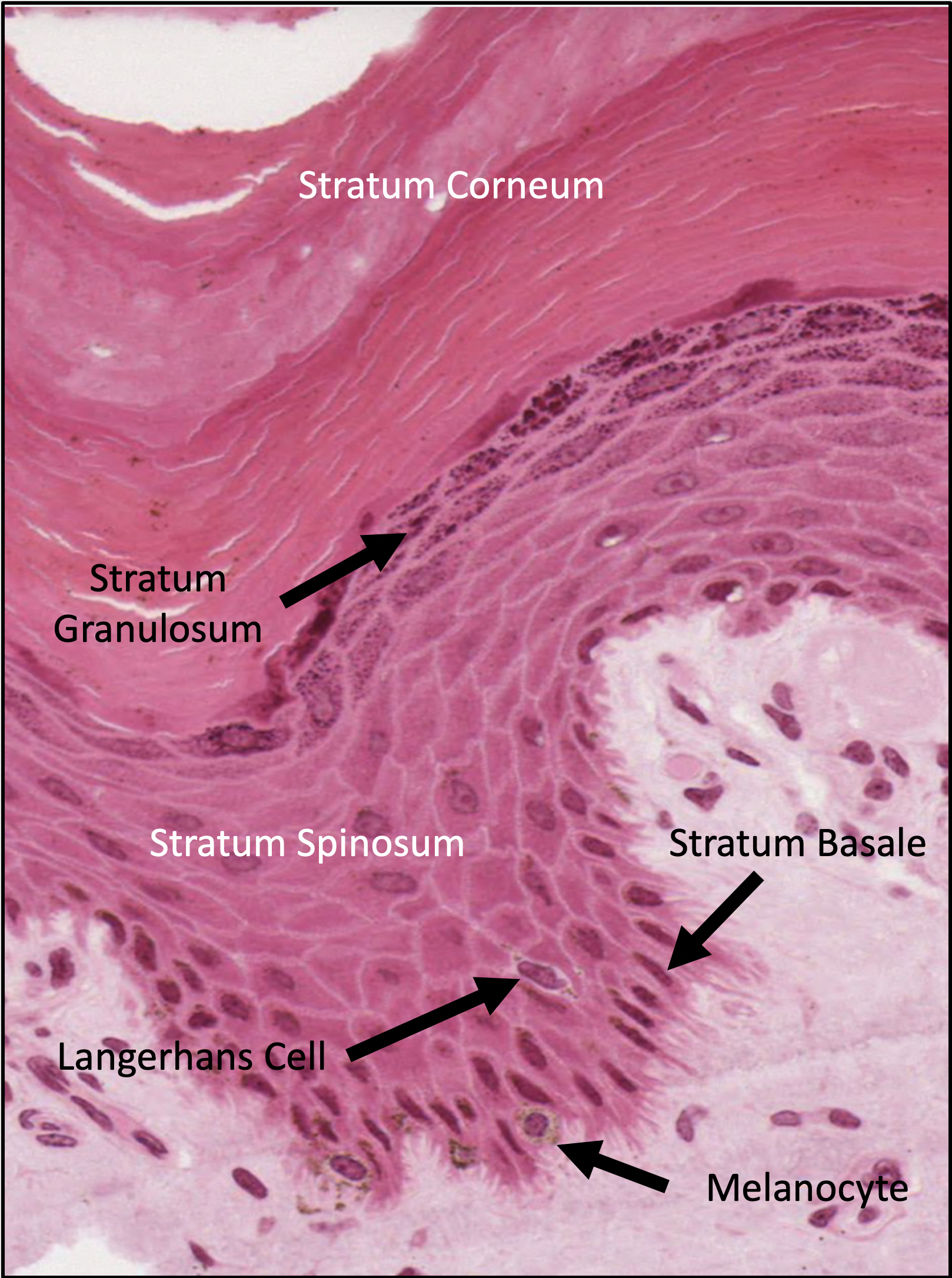
#7. What are the function of Langerhans cells?
Langerhans cells are phagocytic cells derived from the bone marrow. They migrate to skin and wait for antigens to come in contact with the epidermis. The cells will phagocytize the antigens and migrate to neighboring lymph nodes, where they will present the antigen to T lymphocytes to initiate an immune response specific to the antigen.
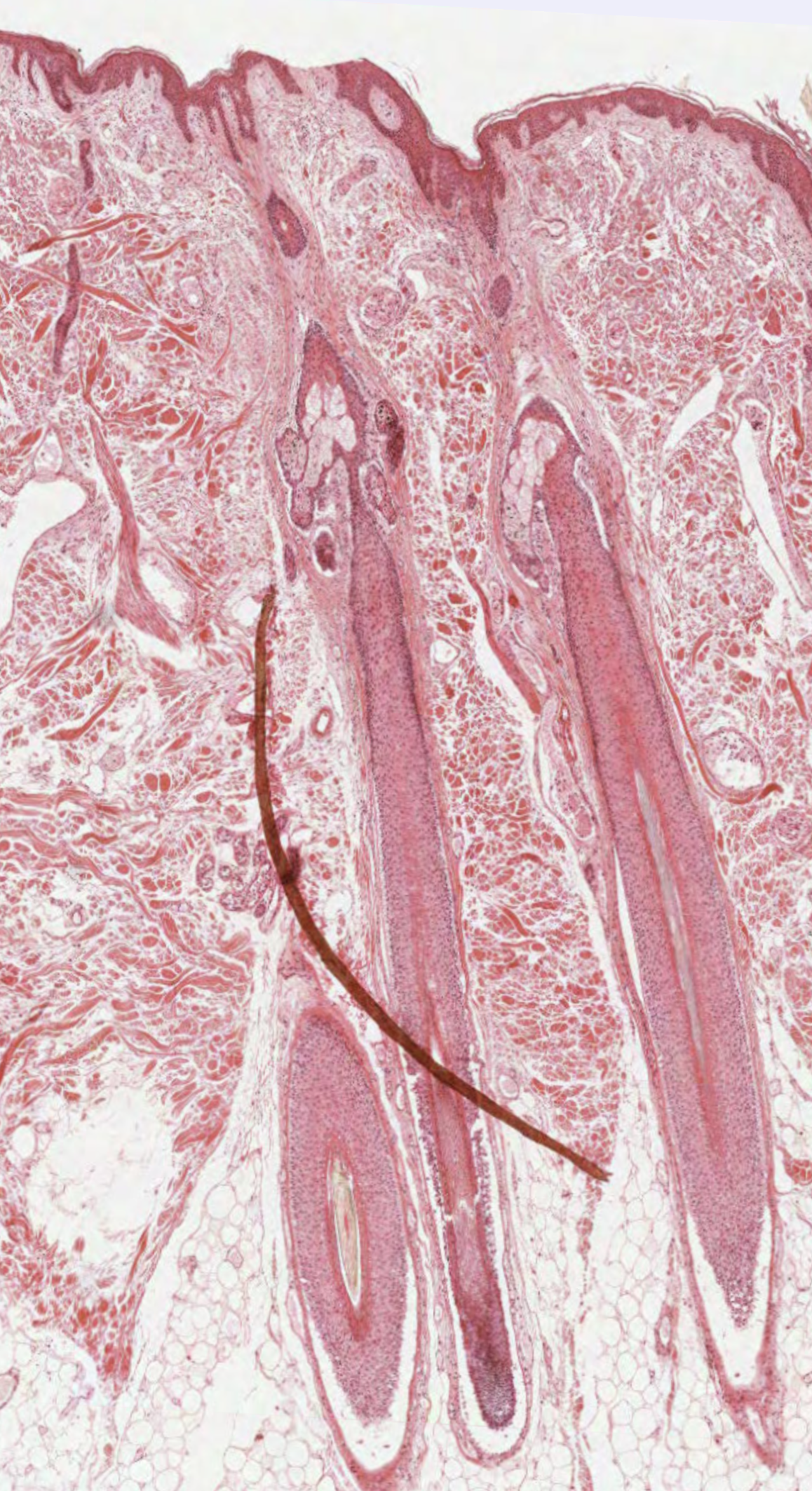
#8. Select the correct skin classification of this histological sample.
Glabrous = non-hairy skin. Therefore, the skin sample is non-glabrous skin due to the presence of the numerous hair follicles that can be seen in the image.
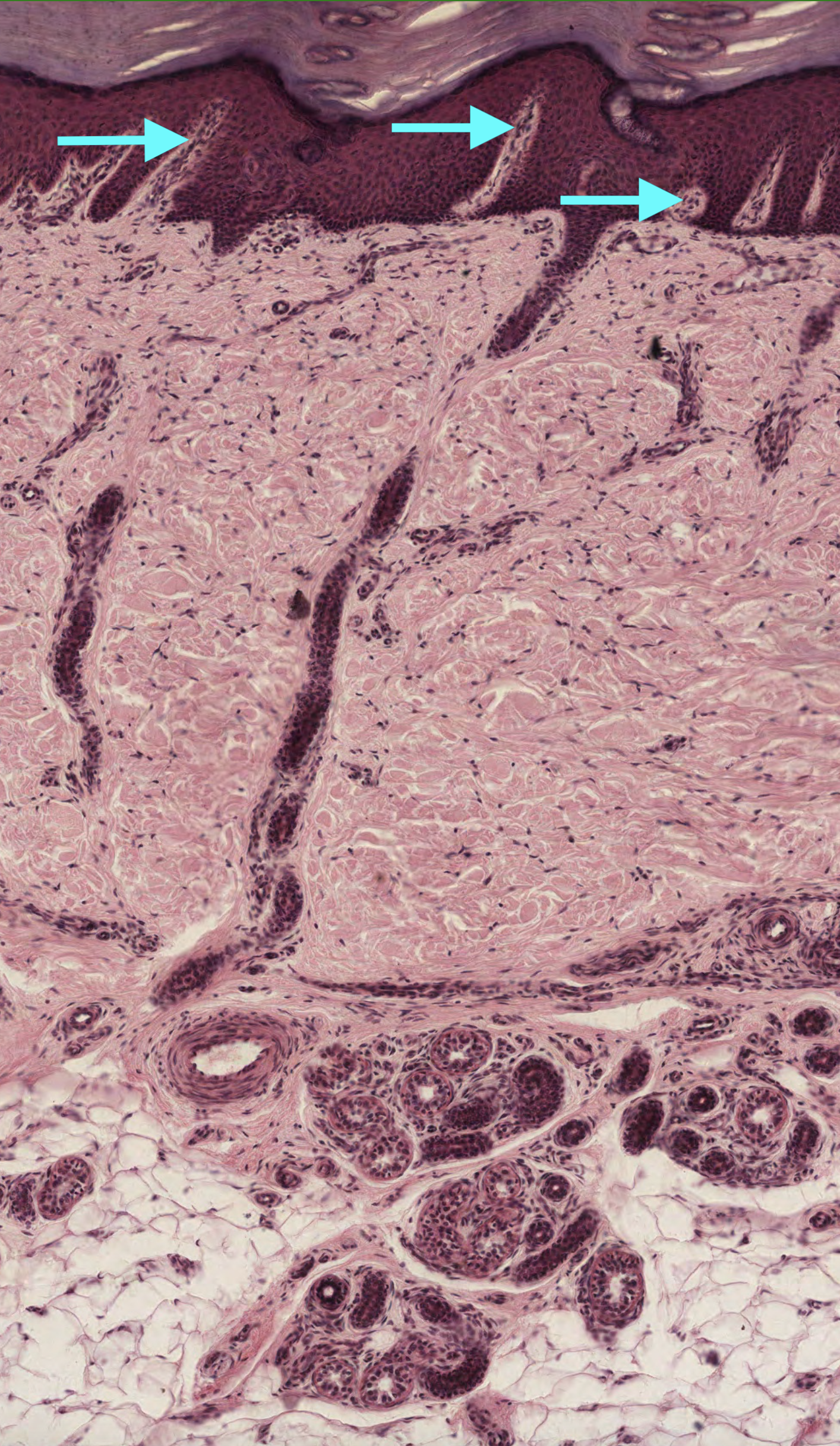
#9. What are the pale stained invaginations indicated by the arrows?
The pale stained regions indicated by the arrows are projections of the papillary dermis known as dermal papillae. They contain blood vessels and are the site of sensory neurons (meissener’s corpuscles). Rete Ridges and epidermal ridges are interchangeable terms and refer to the epidermis, not the dermis.
#10. Melanocytes are typically found in which layer of the epidermis?
Melanocytes appear in the stratum basale layer. They secrete melanosomes, which contain the amino acid tyrosine, which is converted into melanin by the enzyme tyrosinase. Individuals with dark and light skin have similar numbers of melanocytes in their epidermis; however, the rate of melanin production and number of melanosomes is greater in individuals with dark skin.

#11. The epidermal layer that corresponds to the structure indicated as #2 can be correctly identified as the:
Label number 2 indicates the stratum corneum, which is the most superficial layer of the epidermis. The squamous cells of stratum corneum are anucleate cells (don’t contain a cell nucleus or organelles) with a cytoplasm filled with keratin filaments. The extracellular region of these cells are coated with a layer of lipids that assists in the formation of a water barrier of the epidermis.
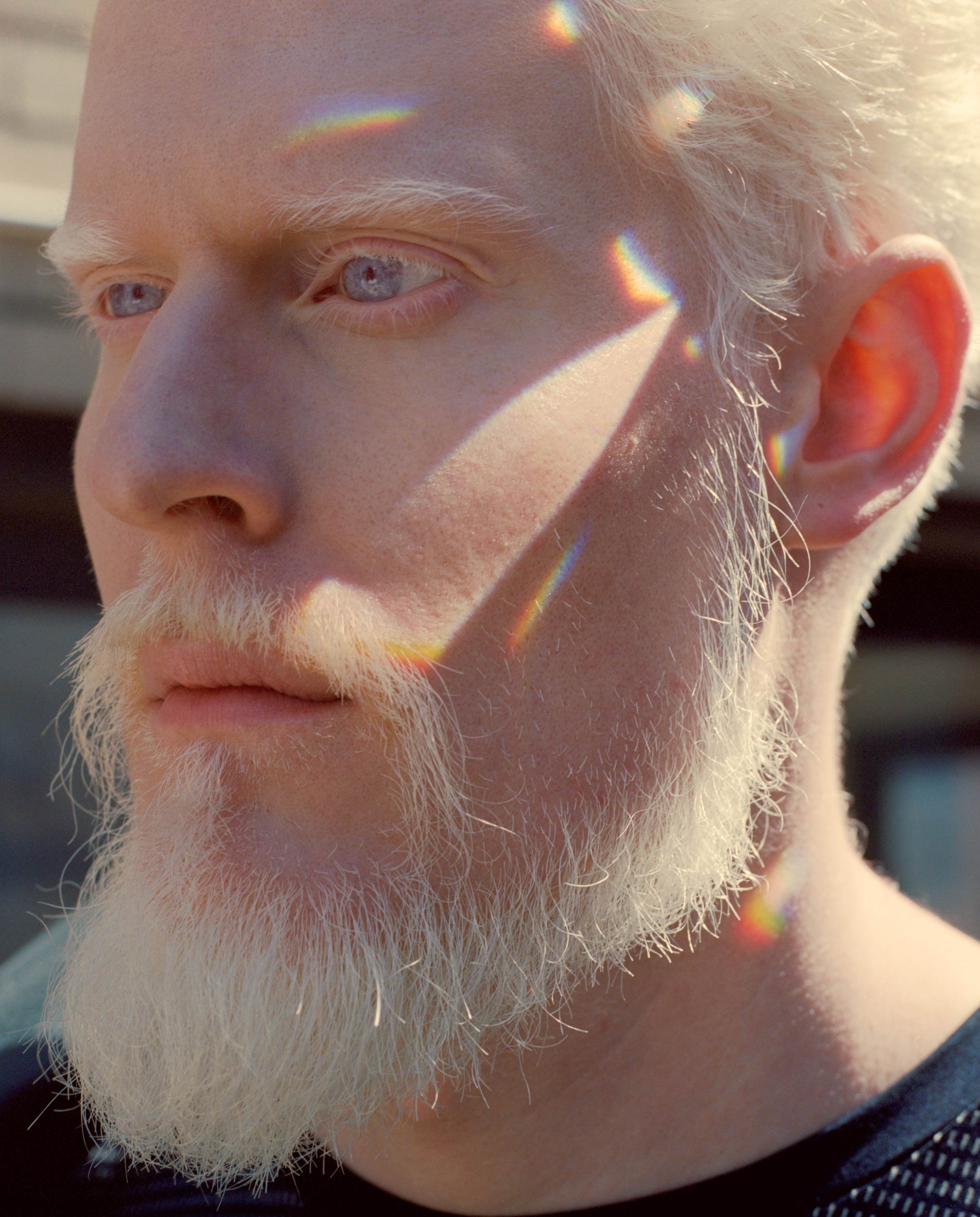

#12. Stephen Thompson is a male model who has albinism. Which of the following is responsible for the lack of pigmentation in his skin?
Melanocytes appear in the stratum basale layer. They secrete melanosomes, which contain the amino acid tyrosine, which is converted into melanin by the enzyme tyrosinase. Individuals with albinism do not produce the enzyme tyrosinase and therefore cannot produce melanin pigment.
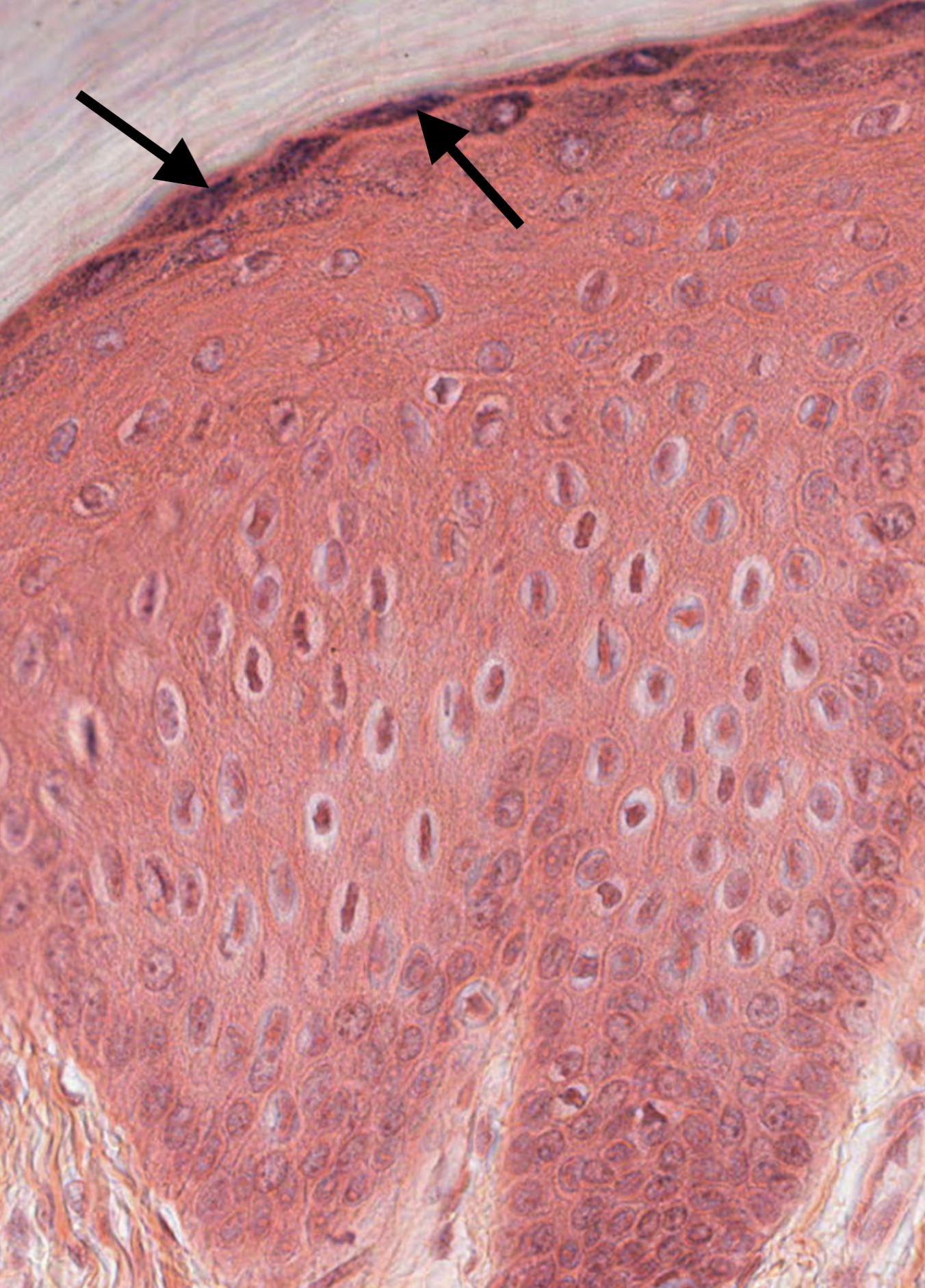
#13. Arrows in the attached image indicate:
The arrows indicate the basophilic keratohyalin granules typical of the stratum granulosum.